how does CBD work in the body?
Introduction
I’ll first throw this scary term in the air: The Endocannabinoid System or simply ECS.
We’ve all heard about the health benefits of CBD and its effects on stress, inflammation & immunity, chronic pain, mood, and more, but have you ever stopped and asked yourself why is it so beneficial?
What actually happens inside your body when you consume CBD oil (or hemp oil)?
Some Human and Cannabinoid Science
Origins and Discovery
The ECS concept emerged during the 60s and 70s, deriving from research into the effects of cannabis on the human body. Researchers isolated various phytocannabinoids from the cannabis plant. Phytocannabinoids are cannabinoids that originate in the plant (phyto).
Studying their effects, scientists discovered a complex network of receptors, enzymes, and biochemical pathways involved in manufacturing and using the body’s own form of cannabinoids. These are the endocannabinoids (endo = originating within the body). Humans share this “system” with most animals, and it evolved almost 600 million years ago.
The Two Basics of the Endocannabinoid System
1. Endocannabinoids (eCBs)
Our nervous system has chemicals that serve as messengers, called neurotransmitters, like serotonin and dopamine. Similarly, our ECS has endocannabinoids (eCBs) that serve as the system’s messengers. They are found all over, circulating in our bodies, with two main such messengers:
- Anandamide: Involved with appetite, memory, pregnancy, and much more.
- Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG): Linked to emotional states, maintaining cardiovascular health, and even protecting from seizures.
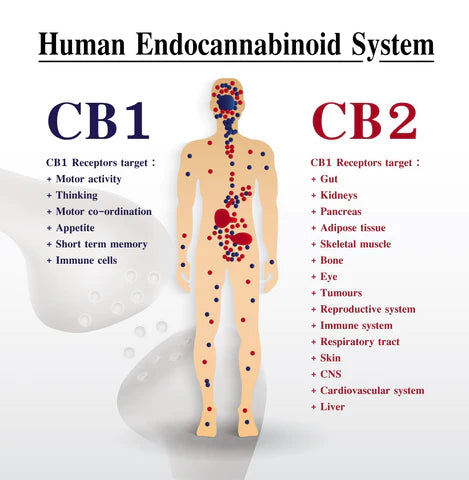
2. Cannabinoid Receptors (CB Receptors)
These receptors reside on the cell’s surface and wait patiently for certain messengers (neurotransmitters) to bind to them. The two main receptors in our endocannabinoid system are CB1 and CB2.
How Do CB1 and CB2 Connect to Our Beloved CBD?
Functionality and Impact
CB1 receptors are all about our brain and are essential for its healthy functioning. These receptors can moderate memory, mood, motor function, or pain perception, depending on the brain region.
CB2 receptors are most often found on the cells of our immune system. They help moderate inflammation and our immune response to pathogens (anything that can produce disease).
When THC binds to CB1 brain receptors, it produces psychoactive properties, leading to a "high." CBD, however, modifies the receptors' ability to bind to cannabinoids rather than directly triggering either CB1 or CB2. This regulation can control activities related to these receptors, such as regulating an overactive immune system or mental sensations like anxiety.
Maintaining and Supporting a Healthy ECS
Modern Lifestyle Impacts
Our ECS is extremely complex, and although research around it has exploded in the past 30 years, the unknown is still greater than the known. However, one thing is sure: our ECS is very easy to throw out of balance, and major causes include stress and diet. Our modern lifestyle does not serve this natural, delicate system well.
Self-Experimentation and Patience with CBD
Finding the Right Balance
Most of us feel that our “system” is not 100% balanced. So how do we fine-tune it? The answer is self-experimentation. There are over 110 cannabinoids in the cannabis plant, each interacting with our CB receptors differently. It’s impossible to “scientifically” predict the effect of these cannabinoids, so self-exploration is the best way to find out what works for you.
True, as science and research advance, we'll likely isolate various cannabinoids and their effects on our receptors and cells. But for now, it’s about finding what works for you. If one oil does not work, try others until you find one that meets your expectations. Don’t expect an overnight miracle. The process takes time until our systems react to cannabinoids’ stimulation.

FAQs
How CBD works in the body?
CBD interacts with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) by modulating receptors' ability to bind to cannabinoids, helping regulate various physiological processes.Is CBD legal?
Yes, CBD is federally legal in the U.S. if it contains less than 0.3% THC, though state regulations can vary.
How does CBD support the immune system?
CBD helps regulate immune responses and reduce inflammation by modulating the endocannabinoid system.
What are the benefits of broad-spectrum CBD?
Broad-spectrum CBD provides the “entourage effect,” enhancing therapeutic benefits by including multiple cannabinoids and compounds from the cannabis plant.
Can CBD help with inflammation?
Yes, CBD has anti-inflammatory properties that can help manage symptoms of inflammation.
Is it safe to use CBD for stress relief?
Consult with a healthcare professional before using CBD, especially for managing chronic conditions or stress relief.Conclusion
Understanding how CBD works in the body involves exploring its interaction with the endocannabinoid system. CBD’s ability to modulate receptors can help manage various conditions, from inflammation to stress. While the science behind CBD is still evolving, its potential benefits are becoming increasingly clear. Stay informed and explore different options to find what works best for you.